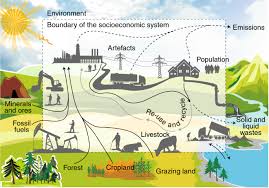
The Role of Sustainability Science in Shaping a Better Future
Sustainability science is an interdisciplinary field that focuses on understanding the complex interactions between human society and the environment to promote sustainable development. It integrates knowledge from various disciplines such as ecology, economics, sociology, and policy-making to address the challenges of environmental degradation, resource depletion, and social inequity.
One of the key principles of sustainability science is the recognition that human well-being is closely linked to the health of ecosystems. By studying these interconnections, researchers in this field seek to develop innovative solutions that balance economic growth with environmental protection and social equity.
At its core, sustainability science aims to provide a framework for decision-making that considers long-term consequences and promotes resilience in the face of global challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and water scarcity. By fostering collaboration between experts from different fields and engaging with stakeholders at all levels, sustainability science offers a holistic approach to addressing complex sustainability issues.
From designing sustainable urban infrastructure to implementing renewable energy solutions, sustainability science plays a crucial role in shaping policies and practices that support a more sustainable future for all. By combining scientific research with practical applications, this field offers hope for creating a world where people can thrive while preserving the planet for future generations.
8 Key Benefits of Sustainability Science for a Resilient and Equitable Future
- Promotes interdisciplinary collaboration among experts from various fields.
- Addresses complex environmental and social challenges through holistic approaches.
- Fosters innovation in sustainable technologies and practices.
- Encourages long-term thinking and planning for a more resilient future.
- Advocates for the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystems.
- Supports sustainable development that balances economic growth with environmental protection.
- Engages stakeholders at all levels to ensure inclusive decision-making processes.
- Offers hope for creating a more equitable and environmentally conscious world.
Challenges in Sustainability Science: Navigating Complexity, Resource Demands, Resistance, and Uncertainty
Promotes interdisciplinary collaboration among experts from various fields.
Sustainability science excels in fostering interdisciplinary collaboration by bringing together experts from diverse fields such as ecology, economics, sociology, and policy-making. This collaborative approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of complex sustainability issues and encourages the development of innovative solutions that consider multiple perspectives. By leveraging the knowledge and expertise of professionals from different disciplines, sustainability science promotes a holistic and integrated approach to addressing environmental challenges, leading to more effective strategies for achieving sustainable development goals.
Addresses complex environmental and social challenges through holistic approaches.
Sustainability science stands out for its ability to tackle intricate environmental and social issues by employing holistic approaches. By recognizing the interconnectedness of ecosystems, economies, and societies, sustainability science offers comprehensive solutions that consider the diverse factors at play. This integrated approach allows researchers and practitioners to address complex challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and social inequality in a more effective and sustainable manner. Embracing a holistic perspective enables sustainability science to develop innovative strategies that not only mitigate current problems but also build resilience for the future.
Fosters innovation in sustainable technologies and practices.
Sustainability science fosters innovation in sustainable technologies and practices by encouraging research and development that prioritize environmental conservation, resource efficiency, and social responsibility. Through interdisciplinary collaboration and a focus on long-term sustainability goals, this approach stimulates the creation of cutting-edge solutions that not only address current environmental challenges but also pave the way for a more sustainable future. By promoting the adoption of innovative technologies and practices, sustainability science drives positive change towards a greener, more resilient society.
Encourages long-term thinking and planning for a more resilient future.
Sustainability science encourages long-term thinking and planning for a more resilient future by emphasizing the importance of considering the impacts of present actions on future generations and the environment. By taking into account the interconnectedness of social, economic, and environmental systems, sustainability science promotes strategies that not only address current challenges but also build resilience to withstand future uncertainties. This proactive approach enables societies to adapt to changing conditions, mitigate risks, and ensure the well-being of both people and the planet in the long run.
Advocates for the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystems.
Sustainability science stands out as a powerful advocate for the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystems. By recognizing the intrinsic value of diverse species and healthy ecosystems, this field emphasizes the importance of protecting natural habitats and promoting conservation efforts. Through research, education, and policy recommendations, sustainability science works towards safeguarding the rich tapestry of life on Earth, ensuring that future generations can continue to benefit from the services and beauty provided by intact ecosystems.
Supports sustainable development that balances economic growth with environmental protection.
Sustainability science excels in supporting sustainable development by striking a delicate balance between fostering economic growth and safeguarding the environment. This approach acknowledges the interconnectedness of economic prosperity, environmental health, and social well-being, emphasizing the importance of long-term sustainability over short-term gains. By integrating knowledge from diverse disciplines and engaging with stakeholders, sustainability science offers innovative solutions that promote a harmonious coexistence between human activities and the natural world, ensuring a resilient future for both current and future generations.
Engages stakeholders at all levels to ensure inclusive decision-making processes.
Sustainability science excels in engaging stakeholders at all levels to ensure inclusive decision-making processes. By involving a diverse range of individuals, communities, organizations, and policymakers in discussions and planning, sustainability science promotes transparency, equity, and accountability in addressing environmental and social challenges. This inclusive approach not only fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment among stakeholders but also leads to more effective and sustainable solutions that consider the needs and perspectives of all involved parties. Ultimately, by embracing inclusive decision-making processes, sustainability science paves the way for collaborative efforts that drive positive change towards a more sustainable future for everyone.
Offers hope for creating a more equitable and environmentally conscious world.
Sustainability science offers hope for creating a more equitable and environmentally conscious world by emphasizing the importance of social equity and environmental stewardship in all aspects of development. By integrating these principles into decision-making processes, sustainability science strives to ensure that economic growth benefits all members of society while safeguarding the health of the planet. Through promoting fairness, inclusivity, and environmental awareness, sustainability science paves the way for a future where people can thrive in harmony with nature, fostering a more just and sustainable global community.
Complexity
The complexity associated with sustainability science stems from the need to integrate diverse disciplines, each with its own methodologies and perspectives. This interdisciplinary approach can make decision-making processes more intricate and time-consuming, as stakeholders must navigate through a myriad of data, theories, and viewpoints to arrive at informed solutions. The challenge lies in finding common ground among experts from different fields and balancing conflicting priorities to achieve sustainable outcomes. Despite the hurdles posed by this complexity, embracing diverse perspectives can ultimately lead to more robust and inclusive sustainability strategies that address the multifaceted nature of environmental and social issues.
Resource Intensive
One notable drawback of sustainability science is its resource-intensive nature. The process of conducting thorough sustainability research and implementing sustainable solutions often demands substantial resources in terms of time, funding, and expertise. Researchers and practitioners in this field may face challenges in securing adequate funding, accessing specialized knowledge, and dedicating the necessary time to develop effective sustainable initiatives. This resource burden can hinder the widespread adoption of sustainable practices and limit the scalability of sustainability projects, posing a significant barrier to achieving long-term environmental and social goals.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a significant con of sustainability science as it poses a challenge to the implementation of sustainability initiatives. Industries and individuals sometimes prioritize short-term economic gains over long-term environmental benefits, leading to reluctance in adopting sustainable practices. This resistance can stem from concerns about increased costs, changes in established processes, or uncertainty about the effectiveness of sustainable measures. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication, education on the long-term advantages of sustainability, and incentives that align economic interests with environmental goals. Addressing this con is crucial for advancing sustainability science and fostering a more sustainable future for all.
Uncertainty
One significant challenge faced by sustainability science is the inherent uncertainty in predicting the long-term outcomes of sustainability actions. The complexity of ecosystems and the interconnected nature of environmental issues make it difficult to foresee all possible consequences of interventions aimed at promoting sustainability. This uncertainty can lead to hesitation in decision-making and implementation, as well as potential unintended consequences that may only become apparent over time. Addressing this con requires a cautious and adaptive approach, emphasizing continual monitoring, evaluation, and adjustment of strategies to navigate the uncertainties inherent in sustainability science.